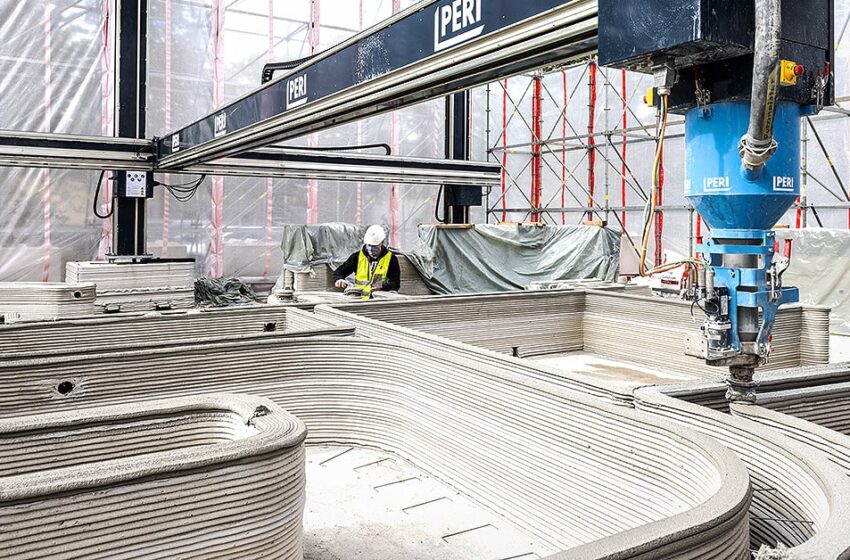
The construction industry is undergoing a technological transformation, and 3D-printed construction materials are at the forefront of this revolution. By leveraging advanced printing technologies, these materials enable faster, more sustainable, and cost-effective construction processes. From homes to bridges, 3D printing is reshaping how we build for the future.
What Are 3D-Printed Construction Materials?
3D-printed construction materials are substances used in additive manufacturing to create building components layer by layer. Common materials include specialized concretes, polymers, geopolymers, and even recycled materials. These materials are designed to work seamlessly with 3D printers, offering precise and customizable building solutions.
How Does 3D Printing in Construction Work?
3D printing in construction involves several steps:
- Design: A digital model is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Material Preparation: A mix of construction material is prepared to achieve the right consistency and properties.
- Printing: The 3D printer follows the digital model, extruding material layer by layer to create the structure.
- Curing and Finishing: The printed structure is cured (if necessary) and finished to meet design specifications.
Types of 3D-Printed Construction Materials
- Concrete:
- Modified concrete mixtures designed for fast setting and extrusion.
- Applications: Walls, foundations, and entire buildings.
- Polymers:
- Lightweight, durable, and versatile materials for non-structural components.
- Applications: Decorative elements, insulation panels, and furniture.
- Geopolymers:
- Sustainable materials made from industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag.
- Applications: Eco-friendly construction and infrastructure.
- Metal Alloys:
- Used in combination with robotic arms for high-strength applications.
- Applications: Bridges, structural supports, and custom components.
- Recycled Materials:
- Plastics, aggregates, or other waste materials reprocessed into printable form.
- Applications: Sustainable construction and temporary structures.
Advantages of 3D-Printed Construction Materials
- Speed:
- Structures can be printed in days instead of weeks or months.
- Accelerates project timelines significantly.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Reduces material waste through precise printing.
- Lowers labor costs by minimizing manual intervention.
- Design Flexibility:
- Enables complex and custom shapes that are challenging with traditional methods.
- Ideal for unique architectural designs.
- Sustainability:
- Promotes the use of recycled and eco-friendly materials.
- Minimizes carbon emissions by reducing transportation and material waste.
- Safety:
- Limits human involvement in hazardous construction environments.
- Reduces accidents on-site.
Applications of 3D-Printed Materials in Construction
- Residential Housing: Affordable, customizable homes printed in record time.
- Infrastructure: Bridges, pedestrian walkways, and tunnels.
- Disaster Relief: Rapidly constructed shelters for emergency scenarios.
- Commercial Buildings: Unique and intricate designs for retail and office spaces.
- Public Art and Monuments: Sculptures and artistic installations.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promise of 3D-printed construction materials, there are hurdles to overcome:
- Material Consistency: Ensuring uniformity in mixes for reliable structural integrity.
- Regulatory Approvals: Navigating building codes and certifications for new materials.
- Printer Scalability: Developing printers capable of handling large-scale projects.
- Skill Gap: Training professionals to design and operate 3D printing systems.
- Cost of Technology: High initial investment in equipment and materials.
The Future of 3D-Printed Construction Materials
As 3D printing technology advances, we can expect:
- Wider Adoption: From large-scale infrastructure to everyday home construction.
- Improved Materials: Development of stronger, more sustainable, and cost-effective mixes.
- Integrated Smart Features: Embedding sensors and smart systems during the printing process.
- Decentralized Manufacturing: Printing on-site to reduce transportation costs and delays.
Conclusion
3D-printed construction materials are more than just a trend; they represent a paradigm shift in how we build. By combining speed, sustainability, and innovation, these materials are paving the way for a new era in construction. While challenges remain, the progress being made is undeniable. The future of construction is here, and it’s being printed, layer by layer.