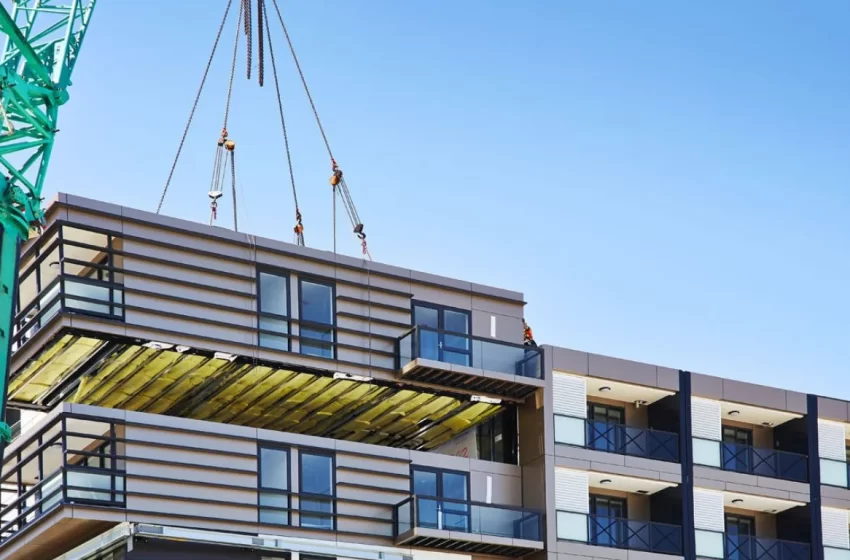
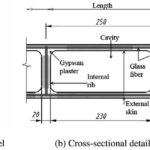
The construction industry has long been known for its slow pace, high costs, and unpredictable timelines. However, modular construction is reshaping the way we build. As a more efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional building methods, modular construction offers numerous benefits that have made it a popular choice for both residential and commercial projects. In this blog, we will dive into what modular construction is, how it works, its benefits, and the various types of modular construction methods that are transforming the industry.
What is Modular Construction?
Modular construction involves the process of creating a building or structure by assembling prefabricated sections, or “modules,” which are manufactured off-site in a controlled factory environment. These modules are then transported to the construction site and connected to form the completed building. Unlike conventional construction, where every component is built on-site from scratch, modular construction combines the benefits of prefabrication with the flexibility of traditional construction.
How Does Modular Construction Work?
Modular construction follows a streamlined process:
- Design and Planning: Modular construction projects begin with designing and planning the building layout. Detailed architectural drawings and specifications are created, often with the help of building information modeling (BIM) software to ensure precise measurements and smooth coordination.
- Factory Prefabrication: The individual modules or units are built in a factory environment, where they undergo strict quality control procedures. This includes building the walls, floors, roofs, and installing plumbing, electrical systems, and insulation. This process typically takes several weeks, depending on the size and complexity of the structure.
- Transportation to Site: Once the modules are completed, they are transported to the construction site. The modular units are delivered on flatbed trucks and are lifted into place by cranes.
- Assembly and Final Touches: The modules are assembled and connected, with finishing touches such as painting, flooring, and exterior cladding completed on-site. The building is then ready for occupancy.
Types of Modular Construction
- Volumetric Modular Construction: This involves the creation of fully enclosed, three-dimensional modules. These modules contain all the necessary components, including internal finishes, windows, and doors. Volumetric modular construction is ideal for projects that require a complete, ready-to-move-in unit, such as hotels, student housing, and residential homes.
- Panelized Modular Construction: In this type of modular construction, only flat panels (walls, floors, and roof sections) are prefabricated in the factory. These panels are then assembled on-site to form the building’s structure. Panelized construction is more flexible and can accommodate larger, more customized designs, making it ideal for commercial buildings and large residential projects.
- Hybrid Modular Construction: Hybrid construction combines elements of volumetric and panelized methods. For instance, the structure of a building might be built using panelized modules, while volumetric units are used for specific areas like bathrooms or kitchens. Hybrid modular construction allows for greater design flexibility while maintaining the efficiency of modular methods.
Benefits of Modular Construction
- Faster Construction Times: One of the primary advantages of modular construction is the significant reduction in construction time. Since the modules are built off-site while the site preparation is happening simultaneously, the overall project timeline is shortened. What would typically take months with traditional methods can be completed in a matter of weeks.
- Cost-Effective: Modular construction can be more affordable than conventional construction due to the streamlined process and reduced labor costs. Additionally, the factory environment allows for better control over material usage, reducing waste and costs. The shortened construction timeline also leads to cost savings in terms of project management, labor, and overhead.
- Quality Control: Manufacturing modules in a controlled factory setting ensures consistent quality and precision. Factory environments are less prone to weather delays or material inconsistencies, resulting in high-quality finished products. Each module undergoes rigorous inspection to meet building codes and standards.
- Sustainability: Modular construction is an environmentally friendly method of building. Because the modules are prefabricated in factories, there is less construction waste generated on-site. Additionally, modular construction can integrate energy-efficient materials, such as insulation, solar panels, and sustainable flooring, contributing to reduced energy consumption in the final building.
- Flexibility and Customization: Modular construction allows for a high level of customization. While the process involves prefabricated modules, the design of those modules can be adapted to fit specific project needs. Whether you’re building a high-rise, a residential home, or a commercial building, modular construction offers the flexibility to accommodate a wide range of styles and sizes.
- Reduced Disruption to the Surrounding Area: Since the majority of the construction takes place off-site, the amount of disruption caused by noise, dust, and traffic is minimized. This makes modular construction ideal for projects in densely populated or urban areas where minimizing disruption is essential.
Applications of Modular Construction
- Residential Buildings: Modular homes are becoming increasingly popular due to their affordability, energy efficiency, and speed of construction. These homes can be customized to meet the needs of homeowners and can range from small single-family homes to large, multi-unit residential buildings.
- Commercial Buildings: Modular construction is widely used in commercial settings, including office buildings, schools, hotels, and healthcare facilities. The modular approach allows for the construction of high-quality, sustainable commercial spaces in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
- Emergency Housing: In disaster-stricken areas, modular construction can provide rapid deployment of temporary or permanent housing. Modular homes can be quickly assembled and are often used to house displaced individuals in the aftermath of natural disasters.
- Healthcare Facilities: Modular construction is being used to build healthcare facilities like hospitals and medical clinics. The speed of construction and ability to provide customized layouts for different departments make modular buildings an ideal choice for the healthcare sector.
- Education: Modular buildings are increasingly used in educational settings, such as classrooms, dormitories, and administrative buildings. Their flexibility allows for easy expansion or reconfiguration of school facilities as student populations grow.
Challenges of Modular Construction
While modular construction offers numerous benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Transportation Limitations: Transporting large modular units to the construction site can present logistical challenges, especially if the site is in a remote or difficult-to-reach location. Special equipment may be required to transport and lift the modules into place.
- Design Restrictions: Although modular construction offers flexibility, there may be limitations when it comes to highly complex or unique architectural designs. Some building codes and zoning regulations may also restrict the use of modular buildings in certain areas.
- Financing and Perception: Some potential buyers or investors may be hesitant to finance modular buildings due to a lack of understanding or misconceptions about the quality and longevity of modular structures. Education and awareness of the benefits of modular construction can help overcome this barrier.
Conclusion
Modular construction is a game-changing methodology that has transformed the way buildings are designed and constructed. With benefits like faster construction times, cost savings, and superior quality control, it’s no wonder that this approach is becoming increasingly popular for residential, commercial, and industrial projects. As technology continues to advance, modular construction will likely become an even more prominent and sustainable solution for the building industry, making it an exciting time for anyone involved in construction.
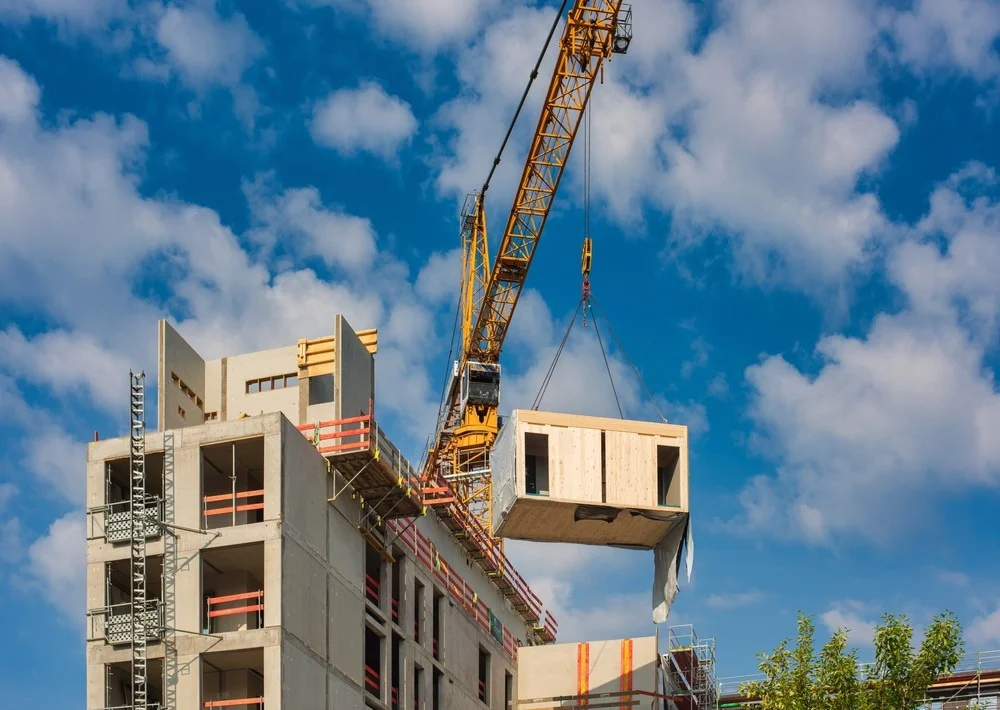

Why Modular Construction is Revolutionizing the Housing Market
The housing market is facing a crisis in many parts of the world, with rising construction costs, labor shortages, and long timelines slowing the production of new homes. Modular construction has emerged as a potential solution to these challenges, offering faster, more affordable, and sustainable housing options. In this blog, we will discuss how modular construction is transforming the housing market, addressing the growing demand for affordable homes and providing opportunities for innovative design.
The Growing Demand for Affordable Housing
In cities and towns worldwide, the need for affordable housing is at an all-time high. Housing shortages are exacerbated by rising land prices, labor shortages, and the slow pace of traditional construction methods. As a result, many people are struggling to find affordable, quality housing.
Modular construction is providing a viable solution to these issues. By utilizing prefabricated modules and factory-controlled processes, modular homes can be built much more quickly and cost-effectively than traditional homes, making them an attractive option for both developers and homebuyers.
The Benefits of Modular Housing
- Speed of Construction: One of the main advantages of modular housing is the speed at which the homes can be built. Unlike traditional construction, which can take months or even years, modular homes are completed in a fraction of the time—often within a matter of weeks. This rapid construction is especially beneficial in addressing the urgent need for housing in high-demand areas.
- Cost-Effective: Modular homes are more affordable than traditional homes, both in terms of initial construction and long-term maintenance. The efficient use of materials, factory-controlled processes, and reduced labor costs all contribute to lower overall expenses. For buyers, this means more affordable housing options, and for developers, faster project completion and higher profit margins.
- Quality Control: With modular construction, homes are built in a controlled factory environment where quality can be closely monitored. The materials used are typically higher quality, and the construction process is streamlined to minimize errors. Additionally, since modules are built off-site, there are fewer risks from adverse weather conditions, ensuring a more consistent and reliable product.
- Sustainability: Modular homes are more sustainable than traditional homes due to their efficient use of materials, reduced waste, and shorter construction times. The prefabrication process minimizes excess material usage, and the ability to incorporate energy-efficient systems—such as insulation, solar panels, and energy-efficient appliances—makes modular homes an environmentally friendly option for buyers.
- Customization and Flexibility: Modular homes are highly customizable. While the modules themselves are pre-built, the layout, finishes, and features can be adapted to suit the specific needs and preferences of the homeowner. This allows for a wide range of designs, from modern, minimalist homes to more traditional, family-oriented layouts.
Modular Construction’s Role in Affordable Housing Initiatives
Many governments and developers are turning to modular construction to help solve the housing crisis. The ability to quickly deliver high-quality, affordable homes is making modular construction an ideal choice for low-income housing projects, urban developments, and disaster recovery efforts.
Modular homes can be mass-produced to meet the growing demand for affordable housing, and since they can be expanded or reconfigured to suit the needs of different communities, they offer long-term flexibility. Furthermore, modular homes can be built in a variety of environments, including remote or urban areas, making them an adaptable solution for a range of housing needs.
Conclusion
Modular construction is revolutionizing the housing market by providing an affordable, sustainable, and efficient alternative to traditional building methods. With its potential to address housing shortages, reduce costs, and accelerate project timelines, modular construction is helping to make homeownership more accessible for many people around the world. As the demand for affordable housing continues to rise, modular construction will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the housing market.