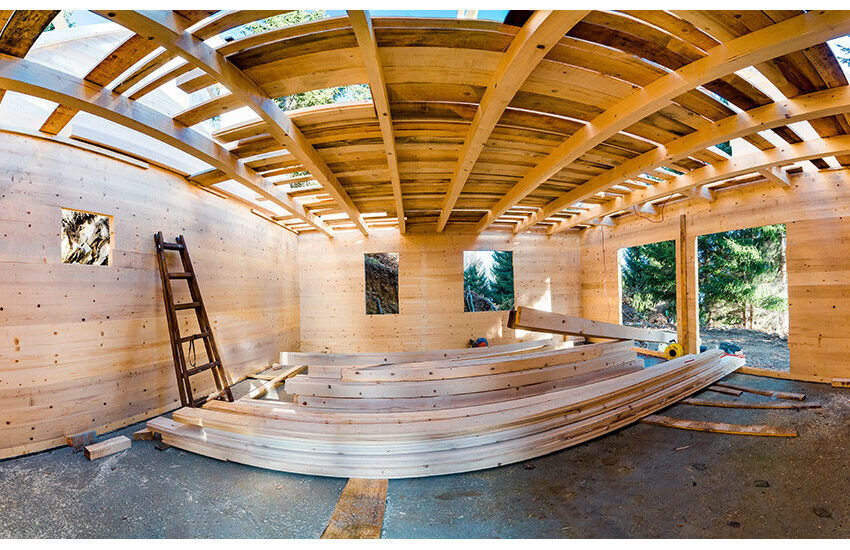
As the construction industry seeks sustainable and innovative solutions, engineered timber, specifically Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT), has emerged as a transformative material. Offering strength, sustainability, and versatility, CLT is reshaping how we approach building design and construction, particularly in the realm of modern wooden structures.
What is Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)?
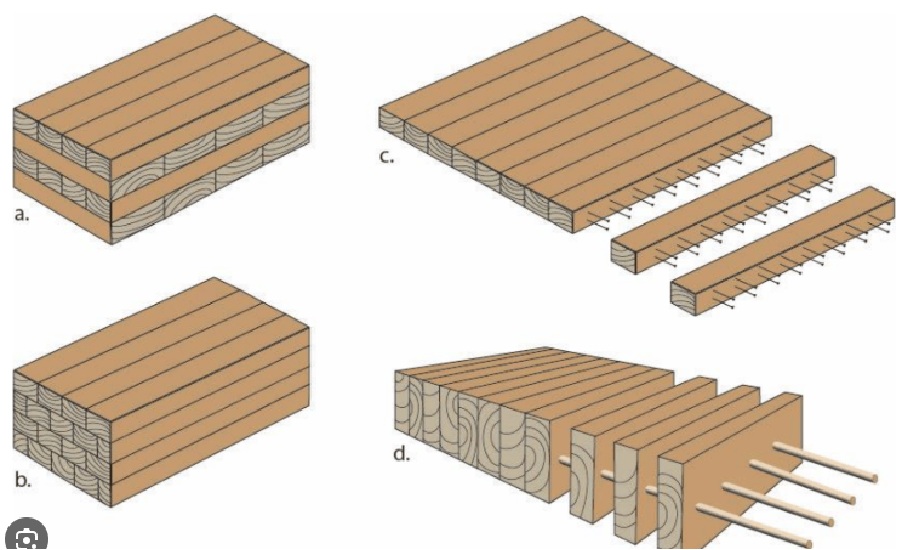
Cross-Laminated Timber is an engineered wood product made by layering boards of solid-sawn lumber in perpendicular directions and bonding them with structural adhesives. This cross-laminating technique enhances strength, stability, and durability, making CLT a viable alternative to traditional materials like concrete and steel.
Properties of CLT
CLT offers a range of impressive properties that make it suitable for diverse construction applications:
- High Strength and Stability:
- The cross-laminated structure provides superior strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Lightweight:
- CLT is significantly lighter than concrete and steel, reducing transportation and foundation costs.
- Fire Resistance:
- Engineered timber chars on the surface when exposed to fire, forming a protective layer that slows combustion.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation:
- Provides excellent thermal performance and soundproofing, enhancing building comfort.
- Sustainability:
- Made from renewable resources, CLT has a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional construction materials.
How is CLT Made?
The production of Cross-Laminated Timber involves the following steps:
- Wood Selection:
- Boards are sourced from sustainably managed forests, typically softwood species like spruce, fir, or pine.
- Layering:
- The boards are arranged in layers, with each layer oriented perpendicular to the previous one.
- Bonding:
- High-strength adhesives are applied between layers to ensure durability and stability.
- Pressing:
- The layered boards are pressed together under controlled pressure and temperature to form large panels.
- Cutting and Finishing:
- Panels are cut to size and finished according to project specifications.
Applications of CLT in Construction
CLT is a versatile material used in various types of construction projects:
- Residential Buildings:
- Ideal for single-family homes and multi-story apartments, offering a warm and natural aesthetic.
- Commercial Structures:
- Used in offices, retail spaces, and schools, showcasing its strength and design flexibility.
- Tall Timber Buildings:
- CLT enables the construction of high-rise wooden buildings, such as skyscrapers, without compromising safety or performance.
- Bridges and Infrastructure:
- Lightweight and strong, CLT is increasingly used in pedestrian bridges and infrastructure projects.
- Renovations and Extensions:
- Prefabricated CLT panels simplify additions and retrofits by reducing construction time.
Advantages of CLT in Construction
- Sustainability:
- CLT is a renewable, biodegradable, and low-carbon material, contributing to eco-friendly construction practices.
- Speed of Construction:
- Prefabricated panels reduce on-site construction time, leading to faster project completion.
- Design Flexibility:
- Large CLT panels allow for open floor plans and creative architectural designs.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality:
- Natural wood surfaces enhance indoor environments by regulating humidity and reducing allergens.
- Reduced Waste:
- Prefabrication minimizes material waste, supporting efficient resource utilization.
Challenges and Limitations
While CLT offers numerous benefits, it also faces some challenges:
- Cost:
- Initial costs may be higher compared to traditional materials, though long-term savings often offset this.
- Moisture Sensitivity:
- Proper detailing and waterproofing are essential to prevent moisture-related issues.
- Regulatory Barriers:
- Building codes in some regions may limit the use of CLT in large-scale or high-rise projects.
- Skilled Labor:
- Construction teams require specialized training to work with CLT effectively.
Future of CLT in Construction
The future of CLT looks promising as technology and awareness continue to advance:
- Carbon-Neutral Construction:
- As the industry prioritizes sustainability, CLT is likely to play a key role in reducing embodied carbon.
- Innovative Designs:
- Architects and engineers are pushing the boundaries of CLT, creating iconic structures that blend sustainability with modern aesthetics.
- Expanded Applications:
- Research into hybrid systems combining CLT with other materials could further enhance its performance.
- Policy and Regulation Updates:
- Revised building codes are expected to accommodate more widespread use of engineered timber in diverse projects.
Conclusion
Cross-Laminated Timber is more than just a construction material; it is a symbol of the industry’s shift toward sustainability and innovation. With its strength, versatility, and environmental benefits, CLT is poised to redefine modern construction practices. As adoption grows, this engineered timber solution will play a pivotal role in creating sustainable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing buildings for future generations