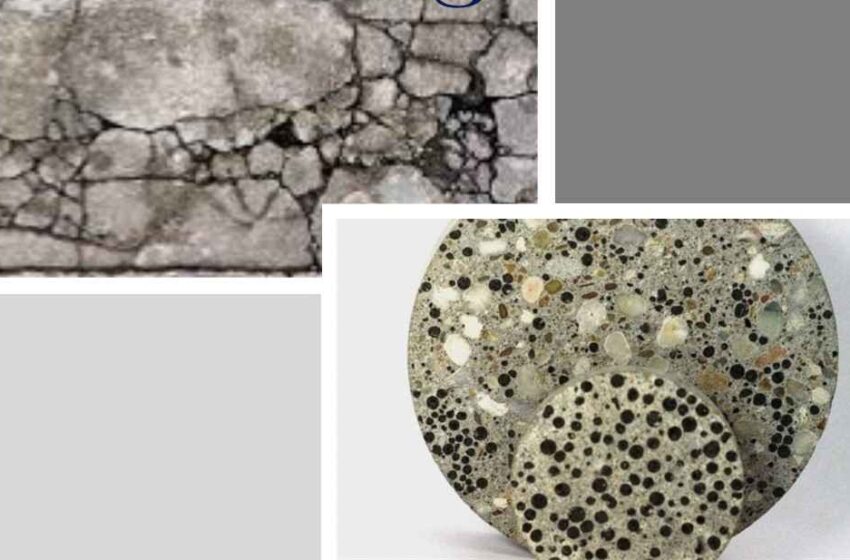
Concrete has been the backbone of modern infrastructure for centuries. From towering skyscrapers to vast highway networks, this versatile material is essential for construction. However, concrete’s biggest weakness has always been its susceptibility to cracking. These cracks, if left unchecked, can compromise structural integrity and lead to costly repairs. Enter self-healing concrete, a revolutionary material that has the potential to transform the construction industry.
What is Self-Healing Concrete?
Self-healing concrete is a smart material designed to repair its own cracks without human intervention. The concept mimics natural healing processes, such as how human skin repairs a cut. By embedding special agents within the concrete, cracks are sealed when they form, restoring the material’s structural integrity.
How Does Self-Healing Concrete Work?
Self-healing concrete employs various mechanisms to repair itself. The most common approaches include:
- Bacteria-Based Healing: Special bacteria (e.g., Bacillus species) are added to the concrete mix along with a nutrient source, such as calcium lactate. When cracks form and water seeps in, the bacteria activate and produce calcium carbonate, which fills the cracks.
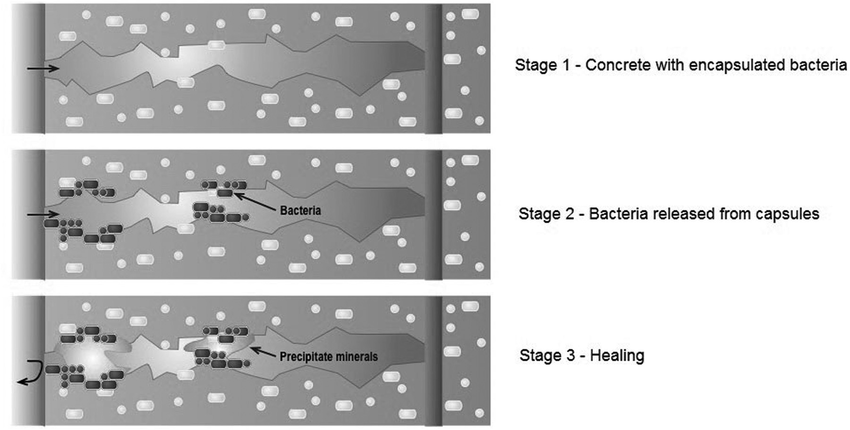
2. Polymer-Based Healing: Microcapsules containing polymers or adhesives are embedded in the concrete. When a crack occurs, the capsules rupture, releasing the healing agent, which then hardens to seal the crack.
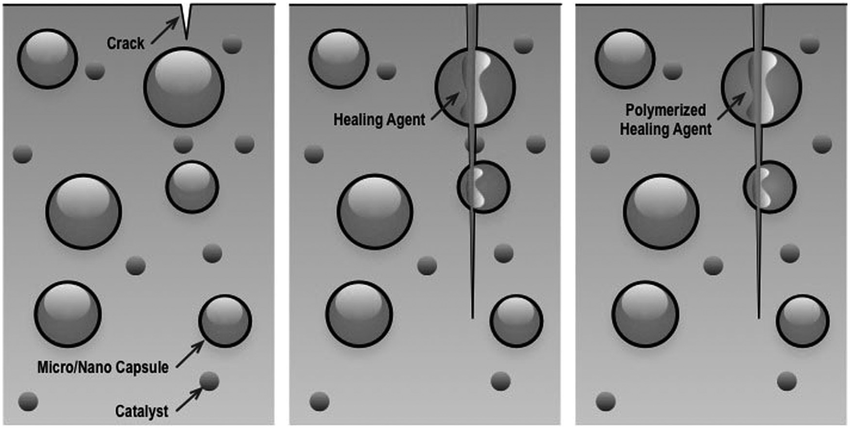
3. Chemical Healing: Self-healing agents like expansive minerals or crystalline compounds are integrated into the concrete. These materials react with water to form solid compounds that fill the cracks.
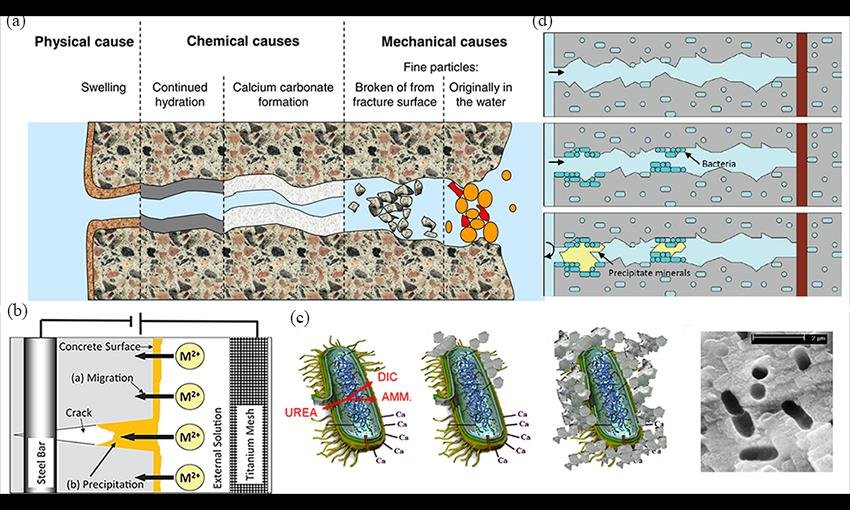
Advantages of Self-Healing Concrete
The benefits of self-healing concrete extend beyond crack repair:
- Durability: By repairing cracks early, self-healing concrete extends the lifespan of structures.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for frequent maintenance and expensive repairs.
- Sustainability: Minimizes material waste and the carbon footprint associated with repair activities.
- Enhanced Safety: Prevents crack propagation that could compromise structural integrity over time.
Applications of Self-Healing Concrete
Self-healing concrete has a wide range of applications:
- Infrastructure: Bridges, highways, and tunnels where cracks can lead to serious structural issues.
- Buildings: High-rise structures and residential buildings for long-term durability.
- Marine Structures: Dams and seawalls that are prone to water-induced damage.
- Industrial Floors: Heavy-load floors in factories and warehouses to avoid frequent repairs.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, self-healing concrete is not without challenges:
- Cost: The initial cost of self-healing concrete is higher than traditional concrete.
- Scalability: Mass production and widespread adoption require further development.
- Performance: Effectiveness varies depending on environmental conditions and the size of cracks.
- Longevity of Healing Agents: Ensuring the bacteria or chemicals remain viable over the structure’s lifespan.
The Road Ahead
Researchers and engineers are continuously working to refine self-healing concrete technologies. Innovations aim to reduce costs, improve effectiveness, and enhance scalability. As these advancements progress, self-healing concrete could become a standard material in construction, offering a sustainable and durable solution to one of the industry’s long-standing challenges.
Conclusion
Self-healing concrete represents a significant leap forward in construction technology. Its ability to autonomously repair cracks has the potential to revolutionize how we build and maintain infrastructure. While challenges remain, the benefits—from reduced maintenance costs to enhanced durability—make it a promising solution for the future. As research continues to advance, we can look forward to a world where our structures are smarter, stronger, and more sustainable.