The construction industry constantly evolves with innovations that improve strength, durability, and efficiency. Among the most promising advancements is the integration of graphene, a groundbreaking material known for its exceptional properties. Graphene-enhanced materials are poised to redefine how we design and build, offering unprecedented benefits across various applications.
What is Graphene?
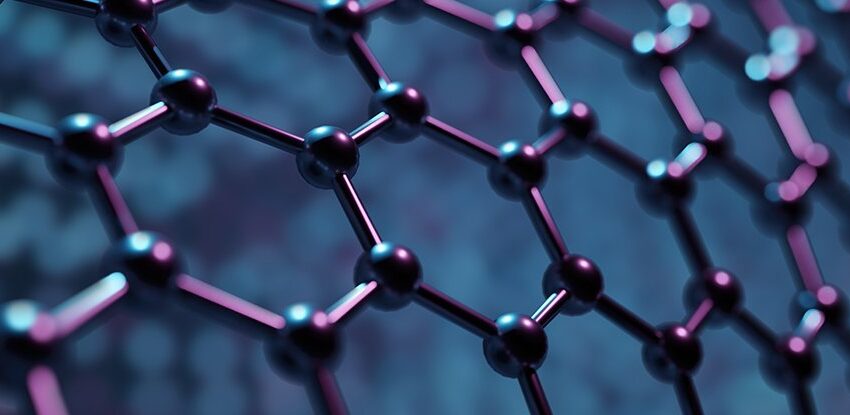
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice. Discovered in 2004, it is the strongest material known to science, yet incredibly lightweight and flexible. Key properties of graphene include:
- Exceptional Strength: Over 200 times stronger than steel by weight.
- Lightweight: Virtually weightless compared to traditional materials.
- Conductivity: Superior electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Flexibility: Can bend without breaking, making it highly versatile.
How Are Graphene-Enhanced Materials Made?
Graphene-enhanced materials are created by incorporating graphene into existing construction materials, such as concrete, steel, and composites. This can be achieved through processes like mixing graphene powders or dispersions with the base material, creating composites that leverage graphene’s extraordinary properties.
Benefits of Graphene-Enhanced Materials
Graphene’s integration into construction materials offers transformative advantages:
- Enhanced Strength and Durability:
- Concrete infused with graphene exhibits higher tensile strength and reduced cracking.
- Steel reinforced with graphene becomes more resistant to corrosion and fatigue.
- Improved Sustainability:
- Reduces the amount of raw material needed while maintaining or enhancing performance.
- Increases the lifespan of structures, minimizing waste and repair needs.
- Thermal and Electrical Properties:
- Graphene-enhanced coatings provide better thermal insulation and energy efficiency.
- Conductive properties open possibilities for smart structures with embedded sensors.
- Lightweight Construction:
- Graphene composites allow for lighter components without compromising strength, reducing transportation costs and energy use.
Applications in Construction
Graphene-enhanced materials are versatile and have diverse applications across the construction industry:
- Graphene-Enhanced Concrete:
- Stronger, crack-resistant concrete that requires less material.
- Ideal for high-rise buildings, bridges, and marine structures.
- Graphene-Coated Steel:
- Corrosion-resistant steel for pipelines, rebar, and structural components.
- Thermal Coatings and Insulation:
- Graphene-based paints and coatings for improved energy efficiency in buildings.
- Smart Structures:
- Graphene’s conductivity enables the integration of sensors to monitor structural health in real time.
Challenges and Limitations
While the potential of graphene-enhanced materials is immense, several challenges must be addressed:
- Cost:
- High production costs of graphene currently limit its widespread adoption.
- Scalability:
- Producing large quantities of high-quality graphene for construction applications remains a technical hurdle.
- Integration:
- Ensuring uniform dispersion of graphene within materials to achieve consistent performance.
- Regulations and Standards:
- The construction industry requires clear guidelines for the use of graphene-enhanced materials to ensure safety and quality.
The Future of Graphene in Construction
Researchers are actively exploring ways to reduce the cost and improve the scalability of graphene production. Advances in manufacturing techniques, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and liquid-phase exfoliation, are making graphene more accessible. As these technologies mature, we can expect a significant uptick in the adoption of graphene-enhanced materials.
Conclusion
Graphene-enhanced materials represent a quantum leap for the construction industry. Their unmatched strength, durability, and sustainability can revolutionize how we build and maintain infrastructure. Although challenges remain, the progress being made is promising. As graphene becomes more affordable and scalable, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of construction, enabling smarter, stronger, and more sustainable structures.